How Healthcare Pricing Is Determined
Healthcare pricing is complex and involves multiple factors, from medical service costs to insurance negotiations. The lack of transparency, variability across providers, and the involvement of multiple stakeholders make healthcare pricing one of the most challenging aspects of the industry. As healthcare costs continue to rise, understanding how prices are set is crucial for employers, insurers, healthcare providers, and patients alike.
This article explores the mechanisms behind healthcare pricing, how prices are determined, and the role of models like reference-based pricing in setting fair, competitive rates.
Factors Influencing Healthcare Pricing
Healthcare pricing is not a straightforward process; it is shaped by a wide range of elements that interact in complex ways. Below are the key factors that influence how prices are determined in the healthcare industry:
Cost of Medical Services
At its core, healthcare pricing is influenced by the actual costs of delivering medical services. These costs include a variety of components, such as:
- Medical staff salaries: Doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals make up a significant portion of healthcare costs.
- Facility expenses: Operating hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities involve costs such as rent, utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses.
- Medical supplies and equipment: Costs associated with medications, surgical tools, diagnostic devices, and other supplies play a major role in determining healthcare prices.
- Technology and innovation: Advanced medical technology and cutting-edge treatments are expensive to develop and maintain, adding to the overall costs of care.
These underlying costs form the basis for healthcare pricing, but they are not the only determining factor. Markups, overhead costs, and adjustments for risk also contribute to the final price patients see.
Insurance Negotiations
Insurance companies play a central role in healthcare pricing. They negotiate reimbursement rates with healthcare providers, which significantly impact the prices paid by patients. These negotiations are often complex, involving factors such as the volume of services, geographic location, and provider networks.
- Fee-for-Service Model: In this traditional model, healthcare providers are paid a specific amount for each service rendered. Insurers negotiate these fees with providers, often resulting in significant price variations for the same service.
- Value-Based Payment Model: This approach ties payments to the quality and outcomes of care, incentivizing providers to deliver better results at lower costs. Value-based pricing aims to align costs with patient outcomes, which can lead to more consistent and reasonable pricing.
Insurance companies also influence pricing through coverage policies, deductibles, and copayments. These factors shape how much patients pay out-of-pocket, which in turn affects demand and overall pricing strategies.
Market Competition
The level of competition in the healthcare market has a substantial impact on pricing. In regions with many healthcare providers, competition tends to drive prices down as providers seek to attract patients. Conversely, in areas with limited provider options, prices are often higher due to reduced competition.
Healthcare organizations also compete on factors such as quality, convenience, and reputation, which can influence pricing. For example, a hospital with a reputation for high-quality outcomes or specialized services may charge higher prices compared to a general hospital. Patients who prioritize quality or specific expertise may be willing to pay more, leading to variable pricing based on perceived value.
Additionally, the rise of urgent care centers, telehealth services, and retail clinics has added a new layer of competition. These alternative care models often offer lower prices for basic medical services, creating more pricing pressure for traditional healthcare facilities.
Read also: Convenient Pharmacy Services for All Your Prescription Needs
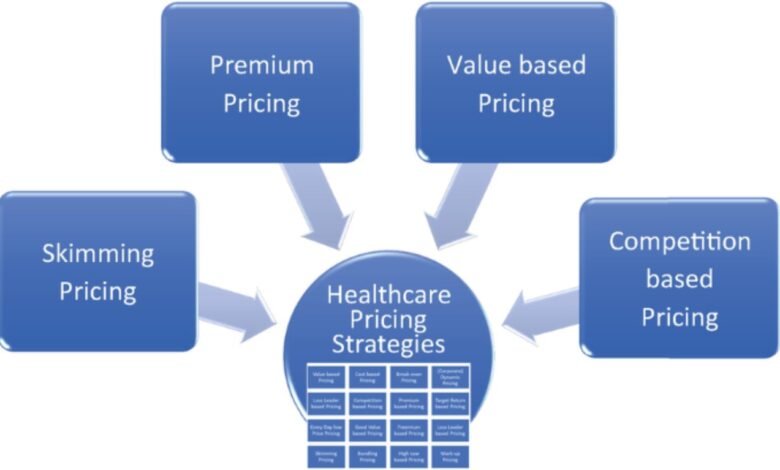
Pricing Models in Healthcare
There are several pricing models used in the healthcare industry, each of which influences how prices are set and adjusted. Below, we examine some of the most common models:
Chargemaster Pricing
The chargemaster is an internal list of prices set by healthcare providers for every service, procedure, and supply offered. It serves as the starting point for billing patients and insurers. Chargemaster prices are typically much higher than the actual reimbursement rates paid by insurers, as they represent the “list price” for services.
While the chargemaster helps hospitals cover costs and negotiate with insurers, it has been criticized for a lack of transparency. Patients often find it difficult to understand how these prices are set and why they vary so widely between providers.
Bundled Payments
Bundled payments are a pricing model where providers receive a single, comprehensive payment for all services related to a specific treatment or condition, rather than separate payments for each service. This model is designed to encourage providers to deliver efficient, coordinated care, as it creates financial incentives to minimize unnecessary services and complications.
Bundled payments can help reduce costs and provide more predictable pricing for patients, as they eliminate some of the variability associated with fee-for-service models. However, implementing bundled payments requires significant coordination among providers, which can be challenging in complex healthcare systems.
Reference-Based Pricing
Reference-based pricing sets a maximum reimbursement amount for specific medical services based on a benchmark, such as Medicare rates or other market-based data. It aims to establish fair prices for services by capping payments at a predetermined level.
Under this model, if a provider charges more than the reference price, the patient is responsible for paying the difference, known as balance billing. This incentivizes patients to seek care from providers who offer services within the reference price range, thereby driving competition and transparency among providers.
Reference-based pricing has gained traction as a way to control healthcare costs and provide more predictable pricing for patients. It also encourages providers to align their charges with market rates, ultimately benefiting both payers and patients.
Challenges in Healthcare Pricing
Despite the various models and factors influencing healthcare pricing, several challenges persist:
Lack of Transparency
One of the most significant issues in healthcare pricing is the lack of transparency. Patients often struggle to find clear, upfront information about the cost of services before receiving care. This makes it difficult for patients to make informed decisions about where to seek treatment and how to manage their healthcare expenses.
To address this challenge, some healthcare providers and payers are investing in price transparency tools that allow patients to compare costs and understand potential out-of-pocket expenses before they receive care. These tools can help patients navigate the complex pricing landscape, although full transparency remains an ongoing goal for the industry.
Variability in Pricing
Healthcare pricing is notoriously variable, even for the same services in the same geographic area. Factors such as hospital reputation, provider experience, and facility type can lead to significant price differences for identical treatments.
Efforts to standardize pricing, such as through bundled payments or reference-based pricing, aim to reduce this variability. However, achieving consistency in healthcare pricing remains a challenge due to differences in provider costs, geographic factors, and patient demographics.
Balancing Cost and Quality
Another challenge is balancing the need to control costs with the need to maintain or improve the quality of care. In some cases, lower-cost providers may deliver care that is less comprehensive or of lower quality. Conversely, higher prices do not always guarantee better outcomes.
To address this issue, value-based care models have emerged, where providers are reimbursed based on patient outcomes rather than the volume of services delivered. This approach aims to align pricing with the quality of care, ensuring that patients receive good value for the money spent.
The Future of Healthcare Pricing
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, pricing strategies will need to adapt to changes in demand, regulation, and technology. Innovations such as telehealth, precision medicine, and artificial intelligence are likely to impact how prices are set and negotiated.
Efforts to improve transparency, reduce variability, and promote fair pricing will play a critical role in shaping the future of healthcare. Models like reference-based pricing, bundled payments, and value-based care are expected to gain further traction as the industry seeks to balance cost control with high-quality patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Healthcare pricing is a multifaceted process influenced by costs, insurance negotiations, competition, and pricing models like reference-based pricing. While challenges such as transparency and variability persist, ongoing efforts to standardize pricing, improve transparency, and align costs with value are driving positive change in the industry.
By understanding how healthcare prices are determined, stakeholders can make informed decisions that benefit both patients and providers. As pricing models continue to evolve, the focus will remain on achieving fair, transparent, and consistent pricing that supports the broader goals of quality care and cost efficiency.